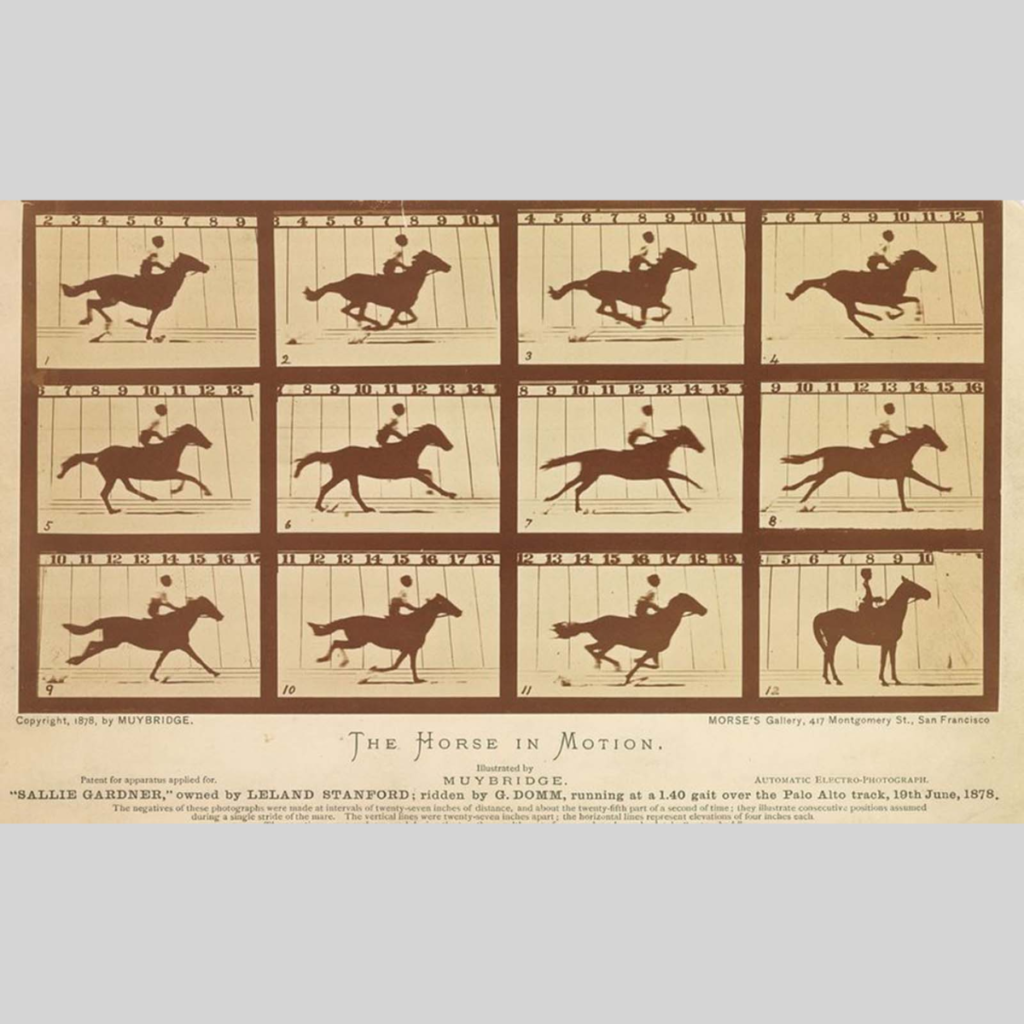

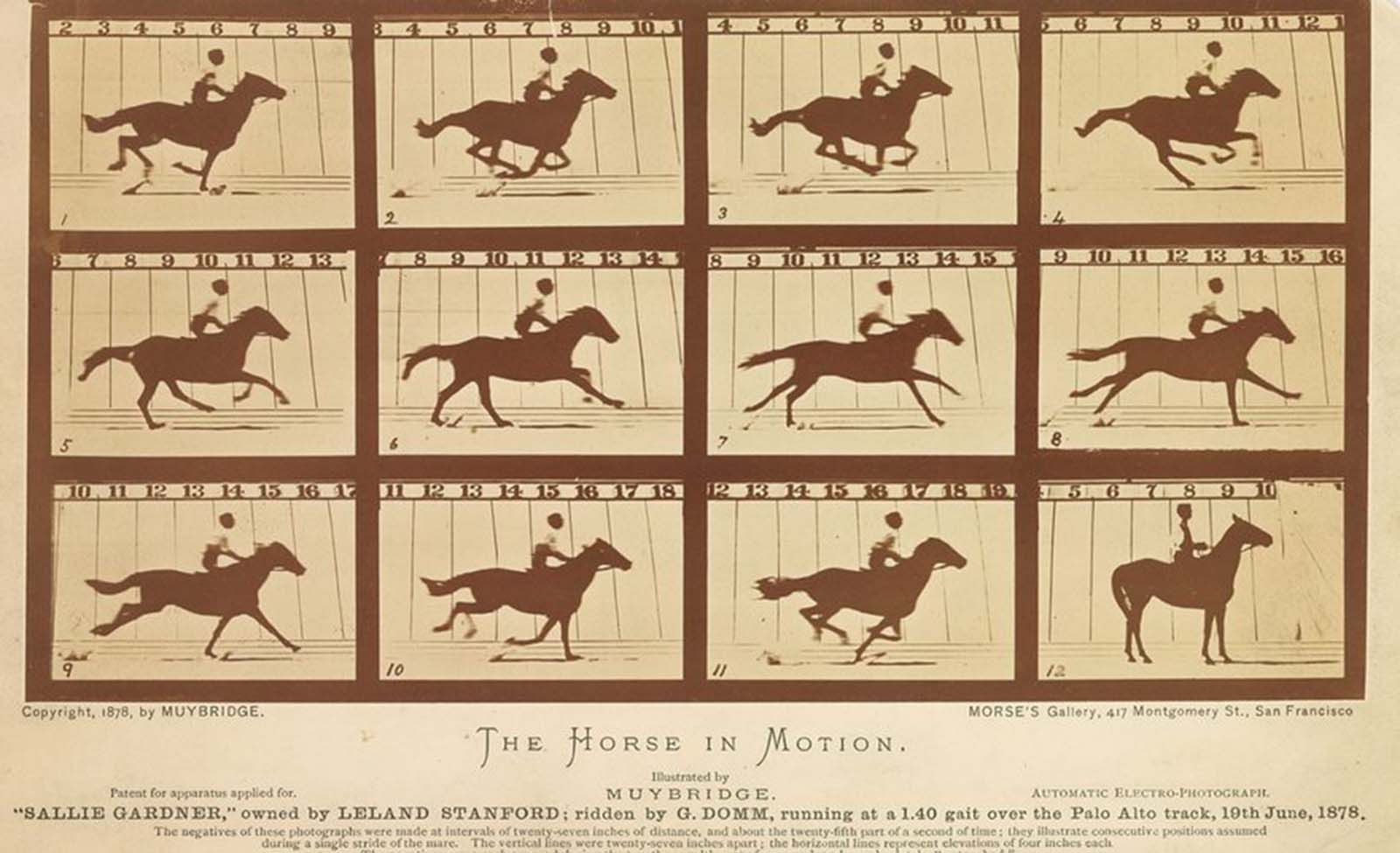
 When a horse trots or gallops, does it ever become fully airborne? This was the question photographer Eadweard Muybridge set out to answer in 1878. Railroad tycoon and former California governor Leland Stanford was convinced the answer was yes and commissioned Muybridge to provide proof.
When a horse trots or gallops, does it ever become fully airborne? This was the question photographer Eadweard Muybridge set out to answer in 1878. Railroad tycoon and former California governor Leland Stanford was convinced the answer was yes and commissioned Muybridge to provide proof.
Muybridge developed a way to take photos with an exposure lasting a fraction of a second and, with reporters as witnesses, arranged 12 cameras along a track on Stanford’s estate.
As a horse sped by, it tripped wires connected to the cameras, which took 12 photos in rapid succession. Muybridge developed the images on site and, in the frames, revealed that a horse is completely aloft with its hooves tucked underneath it for a brief moment during a stride.
The revelation, imperceptible to the naked eye but apparent through photography, marked a new purpose for the medium. It could capture truth through technology. Muybridge’s stop-motion technique was an early form of animation that helped pave the way for the motion-picture industry, born a short decade later.