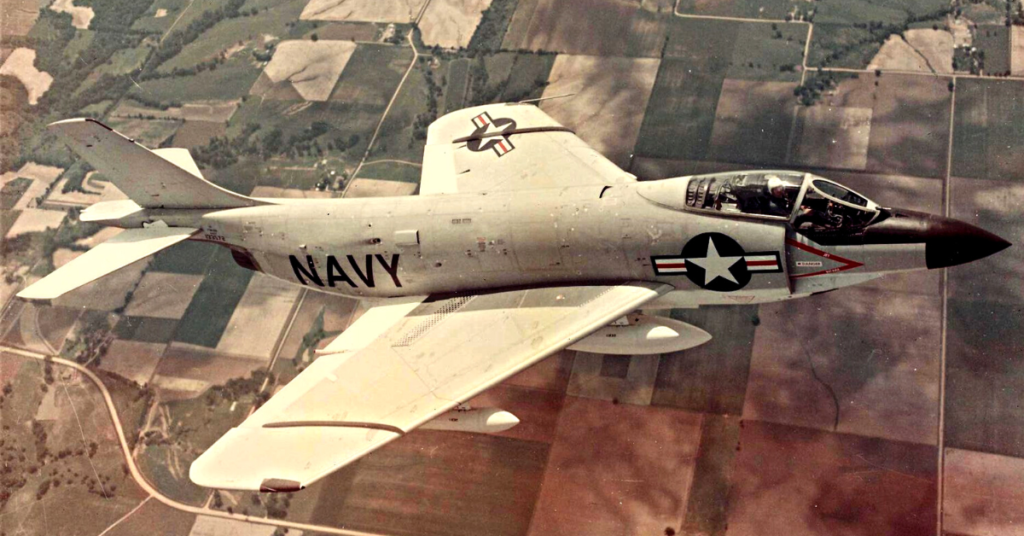

The US Navy has operated an array of aircraft throughout its history, but few had as short a service life as the McDonnell F3H Demon. Developed to counter the powerful fighters coming out of the Soviet Union, its engine issues resulted in several delays. When it was finally ready to see combat, it was already a relic, and, before long, was superseded by the F-4 Phantom II.
Development of the McDonnell F3H Demon
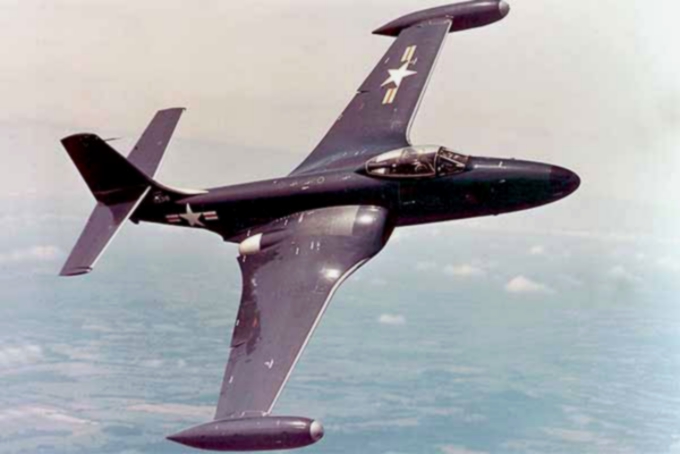

The McDonnell F3H Demon was developed as a replacement for the company’s earlier single-seat, carrier-based F2H Banshee. In 1948, aware the Soviet Union was developing the high-performance Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15, the US Navy issued a call for a swept-wing fighter. The need for such an aircraft only grew when the MiG-15 made its debut in Korea, showing its superiority over the F2H and Grumman F9F Panther.
Before long, prototypes for the F3H began to roll off the production line. It was the first swept-wing design from McDonnell and among the first US aircraft capable of equipping missiles.
Engine issues plagued the development phase
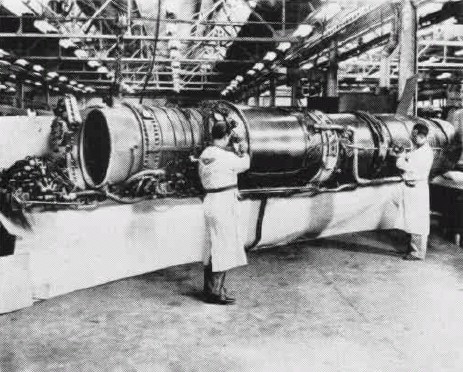
One of the issues that plagued the F3H Demon was its engine. The US Navy had initially envisioned the aircraft equipped with a Westinghouse J40. The appeal was that the J40 would produce more power than traditional engines, and just a single one would be required per aircraft.
However, issues arose upon the J40 being equipped by the F3H. While this can partially be attributed to the aircraft’s weight (it was a hefty 33,900-39,000 pounds), the engine ultimately failed to produce the promised thrust and was unreliable. While numbers vary, there were several recorded instances of J40-equipped F3Hs becoming involved in accidents that resulted in the deaths of their pilots.
All this led the Navy to replace the J40 with the less-powerful Allison J71 engine.
McDonnell F3H Demon specs

With a length of 59 feet and a wingspan of 35.4 feet, the McDonnell F3H Demon was of a similar size to its counterparts. Manned by a crew of one, it could reach a top speed of 716 MPH at sea level and 647 MPH when flying at 30,000 feet. Due to its rather high fuel consumption, it only had an operational range of between 1,180 and 1,370 miles.
From the cockpit, pilots had an unobstructed view of the air around them, affording the F3H the nickname, “The Chair.” It was also given another, less flattering nickname, “Lead Sled,” due to its less than favorable power-to-weight ratio.
The F3H-2 featured AN/APG-51A radar, which saw frequent upgrades as different variants of the aircraft were developed. The F3H’s armament also changed throughout its service life. Originally equipped with four 20 mm colt Mk 12 cannons, the overall total was later decreased to two, to decrease the aircraft’s weight.
Subsequent models, such as the F3H-2M, were armed with missiles – the Raytheon AAM-N-2 Sparrow and, later, the AIM-9 Sidewinder. These later versions were also capable of carrying up to 6,000 pounds of bombs.
A rather short service career
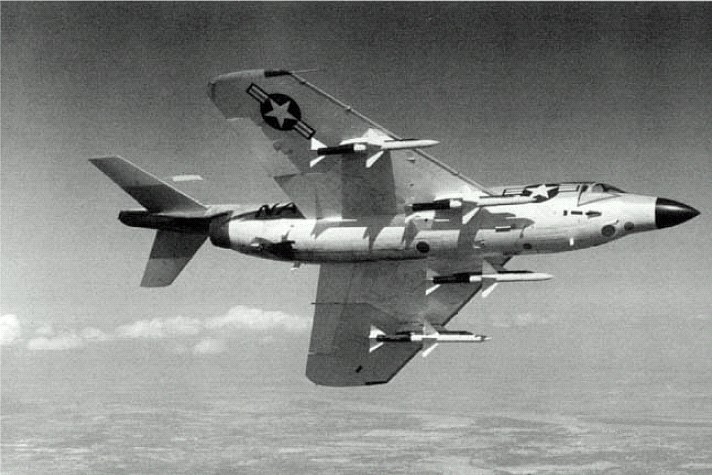

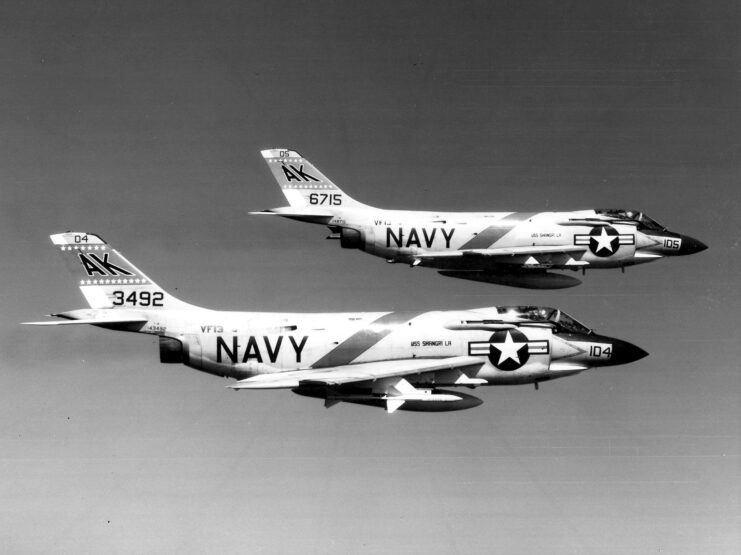
While the F3H Demon didn’t have the supersonic abilities the US Navy had hoped it would, it was still effective as an all-weather, missile-armed interceptor. This meant it was the ideal companion for the service’s day fighters, such as the Grumman F-11 Tiger and the Vought F-8U Crusader.
The F3H saw action in only a handful of conflicts, all of which occurred in 1958. The first was the Lebanese Civil War, a political crisis caused by religious and political tensions in the country. The second was the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, which many view as “the first serious nuclear crisis.” Operating in all conditions, the F3H provided fleet defense over Quemoy Island.
Throughout this time, pilots grew to appreciate the aircraft’s abilities, with the airmen given the nickname, “Demon Drivers.” Those who worked on the F3H were affectionately known as “Demon Doctors.”
Retirement of the McDonnell F3H Demon
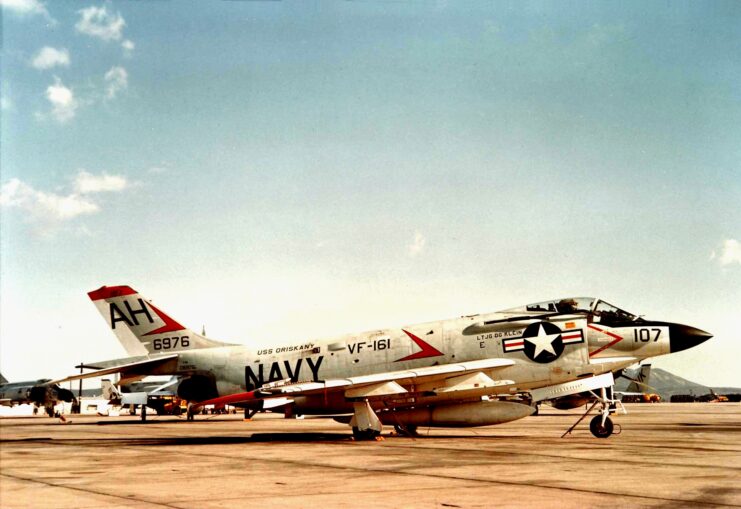

The F3H Demon remained in frontline service with the US Navy until 1962, and it was withdrawn before it could see action in Vietnam. It was replaced by the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II. Viewed as an advanced version of the F3H, the F-4 was just as capable as its predecessor at targeting ground and air targets.
The last F3H-equipped fighter squadron flew the aircraft until September 1964. There are currently three on-display across the United States: at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City; the National Naval Aviation Museum at Naval Air Station Pensacola; and the Pima Air & Space Museum, near Davis-Monthan Air Force Base, Arizona.